61. Real-World Applications of Electrical Engineering Principles
Overview of Electrical Engineering Principles
Introduction to Electrical Engineering
Electrical engineering is a versatile and dynamic field that encompasses the study and application of electricity, electronics, and electromagnetism. It plays a pivotal role in many aspects of our daily lives, shaping modern technology from household items to large power systems. For example, the electricity that powers our homes and the intricate circuits found in smartphones are all products of electrical engineering.
Basic Principles of Electricity
To grasp electrical engineering, it’s essential to understand its foundational concepts:
- Voltage: The electric potential difference between two points.
- Current: The flow of electric charge, measured in amperes.
- Resistance: The opposition to current flow, expressed in ohms.
These principles work together to facilitate the design and operation of various electrical devices and systems, illustrating the core of electrical engineering.

Electrical Engineering in Power Systems
Role of Electrical Engineers in Power Generation
Electrical engineers are integral to the design and operation of power generation systems. They ensure that power plants, whether fossil-fuel, nuclear, or renewable energy sources like wind and solar, operate efficiently. Their responsibilities include:
- System Design: Creating blueprints for power generation facilities.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring adherence to safety and environmental regulations.
This role is crucial as efficient power generation directly impacts energy costs and environmental sustainability.
Transmission and Distribution of Electrical Power
Once generated, electrical power needs to be transmitted and distributed effectively. Engineers oversee the transformation of high-voltage electricity into usable forms for homes and businesses. The process involves:
- Transmission Lines: Carrying electricity over long distances with minimal loss.
- Substations: Reducing voltage to safer levels for local distribution.
These systems ensure that electricity reaches consumers reliably, making electrical engineers vital players in maintaining our modern lifestyle.

Applications in Electronics and Telecommunications
Circuit Design and Analysis
In the realm of electronics, circuit design and analysis form the backbone of innovation. Electrical engineers meticulously create and evaluate circuits that power everyday devices. For instance:
- Analog Circuits: Used in amplifiers and sensors.
- Digital Circuits: Essential for smartphones and computers.
Engineers test these circuits to ensure they function correctly, ultimately improving device efficiency and performance.
Communication Systems and Signal Processing
The transmission of information relies heavily on advanced communication systems. Engineers develop and refine these systems, enabling seamless connectivity through:
- Wireless Networks: Facilitating the use of mobile devices.
- Signal Processing: Enhancing data integrity during transmission.
By applying these principles, electrical engineers make significant contributions to our ability to communicate effectively in an increasingly digital world.

Embedded Systems and Control Engineering
Designing Embedded Systems
Embedded systems are the unsung heroes behind many of our daily gadgets, functioning silently to enhance functionality. Electrical engineers focus on creating these specialized systems, which include:
- Microcontrollers: The brain of devices like washing machines.
- Sensors: Essential for smart home devices, ensuring convenience and efficiency.
By paying attention to design constraints such as power consumption and size, engineers shape how these systems perform in our technology-driven lives.
Control Theory in Electrical Engineering
Control theory is crucial in ensuring that systems operate smoothly and efficiently. Engineers apply these principles to develop algorithms that manage the behavior of dynamic systems, leading to improved accuracy in applications like:
- Robotics: Providing precise movement control.
- Industrial Automation: Streamlining processes in manufacturing.
This aspect of electrical engineering not only optimizes performance but also enhances safety, demonstrating the importance of control systems in modern technologies.
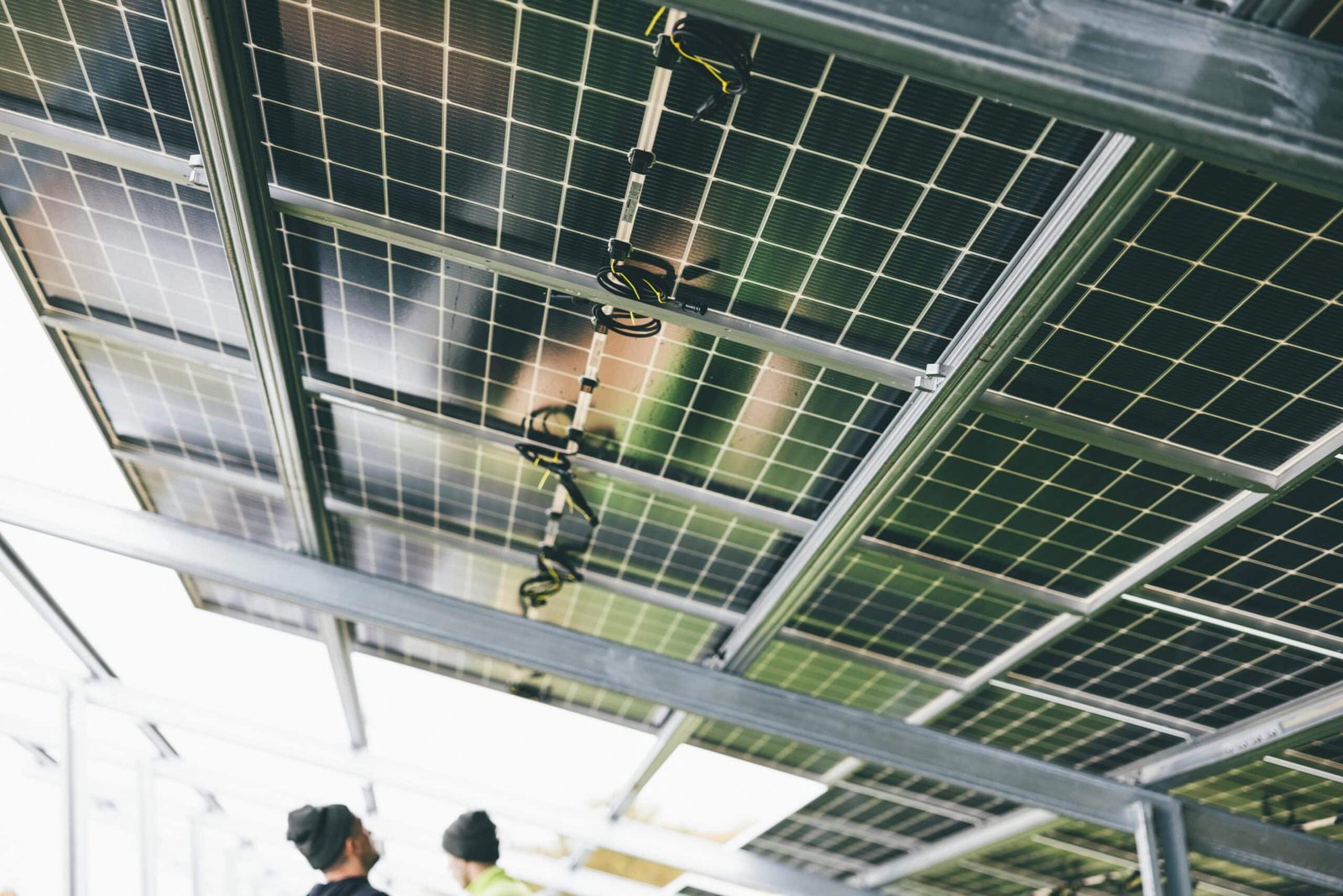

Renewable Energy and Sustainability
Sustainable Energy Sources
As the world shifts towards greener alternatives, electrical engineers play a key role in harnessing sustainable energy sources. Solar, wind, and hydroelectric power are becoming increasingly popular due to their minimal environmental impact. For example:
- Solar Energy: Utilizing photovoltaic cells to capture sunlight.
- Wind Energy: Relying on turbines to convert wind motion into electricity.
These sustainable sources not only reduce carbon footprints but also promote long-term energy security.
Integration of Renewable Energy Systems
The challenge lies in effectively integrating these renewable systems into existing power grids. Engineers focus on:
- Grid Stability: Ensuring a consistent energy supply despite the variability of renewables.
- Energy Storage Solutions: Such as batteries, to store excess energy generated during peak production times.
By effectively integrating renewable energy systems, engineers are paving the way for a more sustainable future, balancing the needs of energy consumption with environmental conservation.



